The kidneys
The kidneys’ vital job is to uphold the body’s fluid balance and chemical environment through filtering the body’s blood. In addition, they produce several hormones.
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs. They are located near the middle of your back, just below the rib cage. The kidney contains approximately one million functional units called nephrons. The nephrons filtrate blood, reabsorb and secrete substances to generate urine.

Role of the kidneys
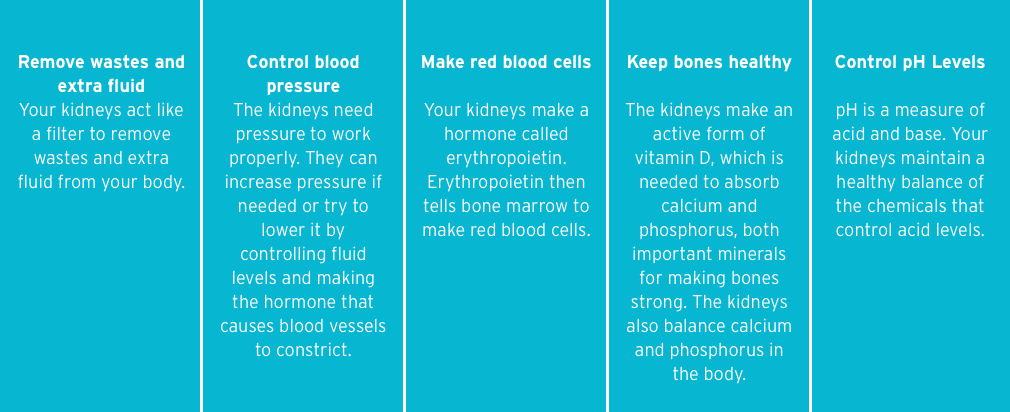
The main purposes of the kidney can be defined by following five pillars:1
---------------------------------
Sources
1 https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/kidney-disease/kidneys-how-they-work
(Accessed 23.06.2022)
Schematic display of a nephron 2
How does it work?
Blood flow through the kidneys is immense which is necessary to fulfil one of the renal tasks and remove all the wastes that accumulate in the blood.
Approximately 1.2 litres of blood passes through the kidneys every minute which means that the kidneys process a total of approximately 1.700 litres of blood per day.1
The blood reaches the kidney via the renal arteries, which divide into many smaller blood vessels. Finally, the blood passes through the glomerular capillaries.
The glomerular capillaries act as a filter and are thereby an important part of the renal filtering system. Because of the pressure exerted by the blood as it flows through the capillaries, components such as water, salts, sugar, and wastes are pressed out of the blood vessels into the space of the Bowman’s capsule. This mixture is called primary urine. The primary urine passes through the tubule. The tubule is surrounded by a network of blood vessels. As it passes through the tubule, most of the components of the primary urine are reabsorbed, depending on the needs of the body. Of the approximate 170 litres of primary urine filtered through the glomerular capillaries during the course of a day, only about 1.7 litres of urine are actually excreted.1
The urine that remains in the tubule is collected in the collecting tubule and transported to the calices of the kidney. From there, the urine reaches the renal pelvis and is transported through the ureter into the bladder, the place of urine storage. The urethra transports the urine out of the body.
---------------------------
Sources
1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279384/
(Accessed 20.01.2021)
2 National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
National Institutes of Health https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-
information/kidney-disease/kidneys-how-they-work
(Accessed 24.02.21)
What is renal function?
Your health care team may talk about the work your kidneys do in terms of "renal function". If you have two healthy kidneys, you have 100 percent of your kidney function. This is more than you really need. Some people are born with only one kidney and are still able to live a normal and healthy life. Many people donate a kidney for transplantation to a family member or friend and continue to have a relatively normal kidney function. Symptoms usually only appear when the kidney function has considerably declined. Small declines in renal function do not necessarily cause a problem.
What does GFR mean?
One common measure of kidney function is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). GFR describes how many milliliters of blood the kidneys are able to filter within one minute. The normal value is 90 ml/min or higher.
Often you will see GFR values with the unit ml/min/1.73 m2, because technically, GFR is expressed in relation to body surface area, which averages 1.73 m2.
If your GFR is too low, your kidneys may not be able to remove enough wastes and extra water from your blood. Your GFR can be estimated from a routine measurement of creatinine in your blood. Creatinine is a waste product formed by the normal breakdown of muscle cells; The level of creatinine in your blood increases, as kidney fuction declines.1
-----------------------------
Sources
1 https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/kidney-disease/kidneys-how-they-work
(Accessed 23.06.2022)
The normal GFR value is 90 ml/min or higher.