Dünya nüfusunun %8 -16'sının KBH hastası olduğu tahmin edilmektedir.1
------------------------------------------------
Sources
1 Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K et al. Chronic kidney disease:
global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 2013; 382: 260-72
What ist chronic kidney disease?
Chronic kidney disease (CKD), also known as chronic renal disease, is a condition that occurs when your kidneys don’t work as well as they should to excrete waste, toxins and excess fluid from your body.
CKD is characterised by a progressive loss of kidney function over time.
The end stage kidney disease (ESKD), end stage renal disease (ESRD) or kidney failure, may develop over many years or within only a few months. At this stage, you will require either dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Causes of CKD
Kidney disease is usually caused by other pre-existing health problems, which put pressure on the kidneys. Commonly, it is a combination of different health problems.
CKD becomes more common with increasing age (> 60 years with variations worldwide). Although older people are more likely to suffer from chronic kidney disease, it can be developed at any age.1
------------------------------------------------
Sources
1 https://www.kidney.org/news/monthly/wkd_aging (accessed 20.01.2021)
2 https://www.kidneyfund.org/prevention/are-you-at-risk/ (accessed 20.01.2021)

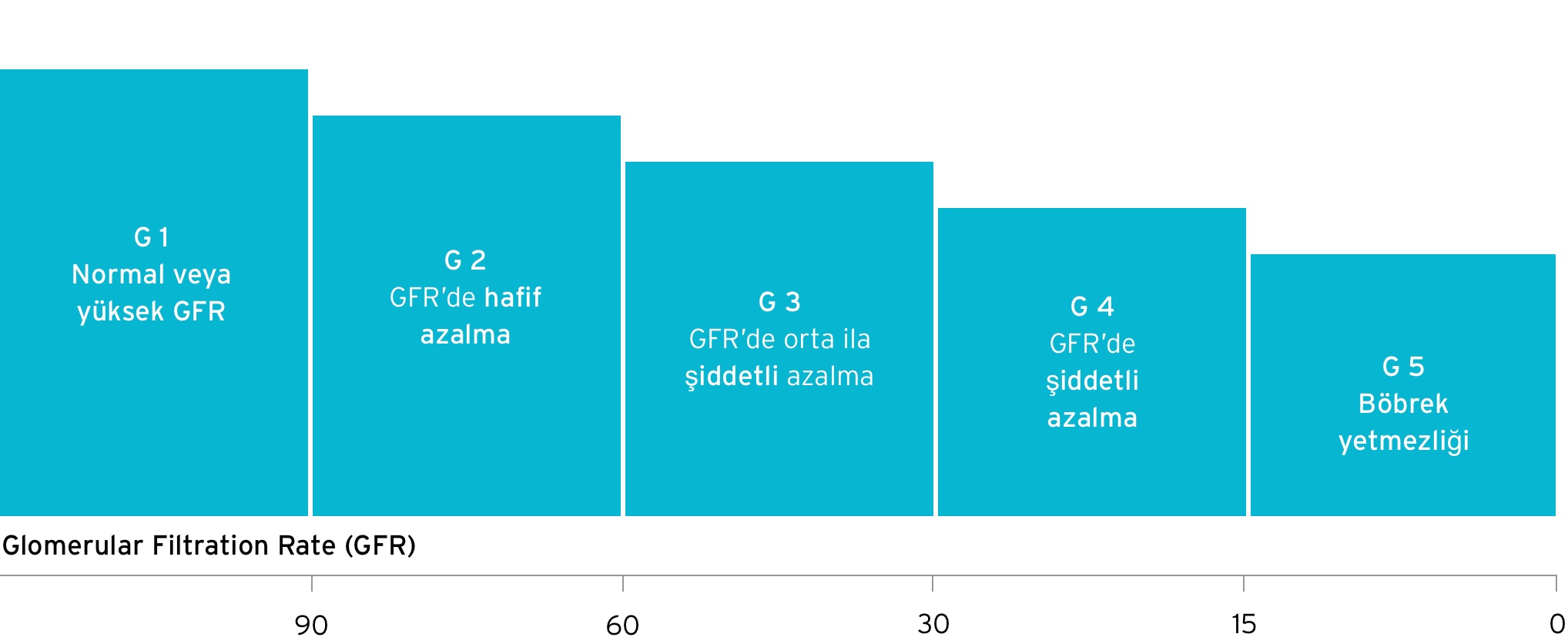
Stages of CKD
Defined by the level of the kidney function (glomerular filtration rate, GFR), there
are five stages of chronic kidney disease (according to the KDIGO Guidelines1). G 1
(GFR >= 90 ml/min/1.73 m2) is the earliest stage, while G 5 (GFR < 15 ml/min/1.73
m2) represents kidney failure. This stage is also called end-stage kidney disease
(ESKD) or end-stage renal disease (ESRD). At this point, your have only about 10
-15% of your kidney function left and a renal replacement therapy such as dialysis
is necessary for survival.2
By definition CKD starts at a eGFR <60ml/min/1.73m2 - G 31. Most patients may not
have any severe symptoms until their kidney disease is advanced.3 Endocrine/
metabolic derangements or disturbances in the water or electrolyte balance
become visible only in later stages (G4+: GFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2).
CKD stages
------------------------------------------------
Sources
1 Kidney Disease: Improving GlobalOutcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
Clinical Practice Guideline for theEvaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney
Disease. Kidney Inter, Suppl. 2013; 3: 1-150.
2 National Kidney Foundation https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/hemodialysis (accessed 04.01.2021)
3 National Kidney Foundation www.kidney.org/atoz/content/about-chronic-kidney- disease (accessed 03.12.2020)
Diagnosis
Since a person can have kidney disease without any symptoms, your doctor may
initially detect the condition through routine blood and urine tests. Testing is the
only way to know if you have CKD.
Urine test
A urine test is one type done to check the levels of substances called albumin and creatinine in your urine – they are put in relationship and expressed as the Albumin to Creatinine ratio, or ACR.
Proteins (albumin is of blood protein) usually do not appear in the urine and are therefore a marker of kidney damage. If this test is repeatedly “positive” for protein over a period of three months or more, it is a sign of kidney disease.
Blood test
Böbrek hastalığı için esas tetkik, kan tetkikidir. Tetkik, kandaki kreatinin düzeyini ölçer. Hekimler kan tetkiki sonuçlarının yanında yaş, boy, kilo, cinsiyet ve benzeri yardımcı parametreleri kullanarak kişinin böbreklerinde dakikada kaç mililitre kan süzülebildiğini hesaplar.
Doğrulanmış formüllerle yapılan bu hesaplamanın sonucunda tahmini glomerüler filtrasyon hızına (eGFR) ulaşılır.
Kreatinin, kas hücrelerinin bir yıkım ürünüdür. Belirli bir böbrek hastalığı düzeyine ulaşıldığında kandaki kreatinin düzeyi, böbrek işleviyle korelasyon gösterir.
Bir desilitre kanda kaç miligram kreatinin (mg/dl) olduğunu görmek için laboratuvarlarda kan tetkikleri yapılır. Kandaki kreatinin düzeyleri değişkenlik gösterebilir ve her laboratuvarın kendi normal aralığı vardır; bu aralık genellikle 0,7 mg/dl ile 1,3 mg/dl (61,9-115 µ mol/L) arasındadır.1 Eğer kreatinin düzeyiniz bu aralığın hafifçe üzerindeyse, muhtemelen herhangi bir sağlık sorunu yaşamazsınız, ancak bu yükseklik böbreklerinizin tam kapasiteyle çalışmadığının bir göstergesi olabilir.
------------------------------------------------
Sources
1 MSD Manuals https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/resources/normal- laboratory-values/normal-laboratory-values
(Accessed 03.12.2020)
Check your eGFR Value
Further diagnostics
Once CKD is identified, your doctor will try to find the underlying cause of the disease. This is important, since treating the cause can help to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease.
There are many different diagnostic techniques that can be used, for example imaging techniques (ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging) and several different kinds of blood tests. In some cases, it may be necessary to perform a biopsy, i.e. to remove a tiny piece of the kidney to examine it under a microscope and see how much kidney damage has occurred.1
------------------------------------------------
Sources
1 https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/about-chronic-kidney-disease (Accessed 04.01.2021)